Soil Liquefaction and Its Consequences During Earthquakes: A Historical Overview

Introduction
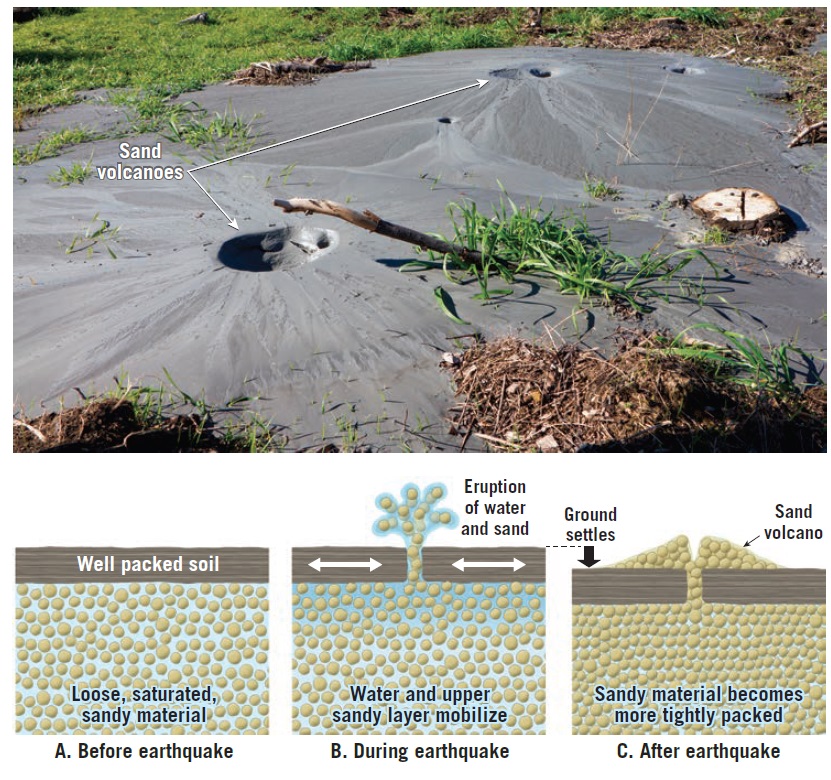
Soil liquefaction is a phenomenon that occurs when soil loses its strength and stiffness due to sudden stress changes such as those caused by earthquakes or other types of vibrations. This can result in significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and other types of structures, as well as loss of life. In this article, we will explore the history of soil liquefaction and its consequences during earthquakes, including some of the most significant events in which soil liquefaction has occurred.
Liquefaction Throughout History
Soil liquefaction is not a new phenomenon. Historical records indicate that liquefaction has been observed in several parts of the world for centuries. One of the earliest recorded instances of soil liquefaction was in the Chinese city of Kaifeng in 1642, where an earthquake caused sand boils and subsidence. Similar events have been observed in other parts of the world, including the Lisbon earthquake of 1755, which caused soil liquefaction in several parts of the city.
One of the most significant events in the history of soil liquefaction occurred during the 1964 Alaska earthquake. The earthquake, which had a magnitude of 9.2, caused widespread liquefaction in the Anchorage area, resulting in significant damage to buildings and infrastructure. The event led to the development of new techniques for mitigating soil liquefaction, such as the use of ground improvement methods.
Soil Liquefaction in Modern Times
Soil liquefaction continues to be a significant problem in many parts of the world. One of the most recent events in which soil liquefaction has occurred was the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan. The earthquake, which had a magnitude of 9.0, caused widespread liquefaction in the Sendai area, resulting in significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and other structures.

In addition to earthquakes, soil liquefaction can also occur due to other types of stress changes, such as those caused by traffic or construction. In urban areas, soil liquefaction can be a significant problem due to the high concentration of structures and infrastructure. This has led to the development of new methods for mitigating soil liquefaction, such as the use of ground improvement techniques and liquefaction-resistant foundation designs.
Conclusions
Soil liquefaction is a significant problem that can result in significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and other structures, as well as loss of life. While soil liquefaction has been observed throughout history, it continues to be a problem in modern times, particularly in urban areas. As such, it is essential to continue to develop new methods for mitigating soil liquefaction and to educate people about the risks and consequences of soil liquefaction during earthquakes and other types of stress changes. By doing so, we can reduce the impact of soil liquefaction on society and the environment.
