What are anticlines and synclines?

The difference between Anticlines and synclines
Anticlines and synclines are geological structures that result from the folding of rock layers in the Earth’s crust. They are both types of folds, which are bends or curves in rock formations caused by tectonic forces. Here’s a brief explanation of each:
Anticlines:
- Definition: Anticlines are upward-arching folds in the Earth’s crust where the oldest rock layers are found in the center or core of the fold.
- Formation: They are typically formed by compressional tectonic forces that act horizontally, causing the rocks to bend and fold upwards. The crest or highest point of the fold is called the anticlinal axis.
- Characteristics: Anticlines often create structures resembling an arch or a dome, and they are associated with the accumulation of various resources such as oil and gas due to the upward migration of fluids within the fold.
Synclines:
- Definition: Synclines are downward-arching folds in the Earth’s crust where the youngest rock layers are found in the center or core of the fold.
- Formation: Similar to anticlines, synclines are also formed by compressional tectonic forces, but in this case, the rocks bend and fold downwards. The lowest point of the fold is called the synclinal axis.
- Characteristics: Synclines typically have a trough-like appearance and are often associated with the deposition of sedimentary rocks in the central part of the fold. They are important in understanding the geological history of an area.
The two most common types of folds are anticlines and synclines (Figure 1).
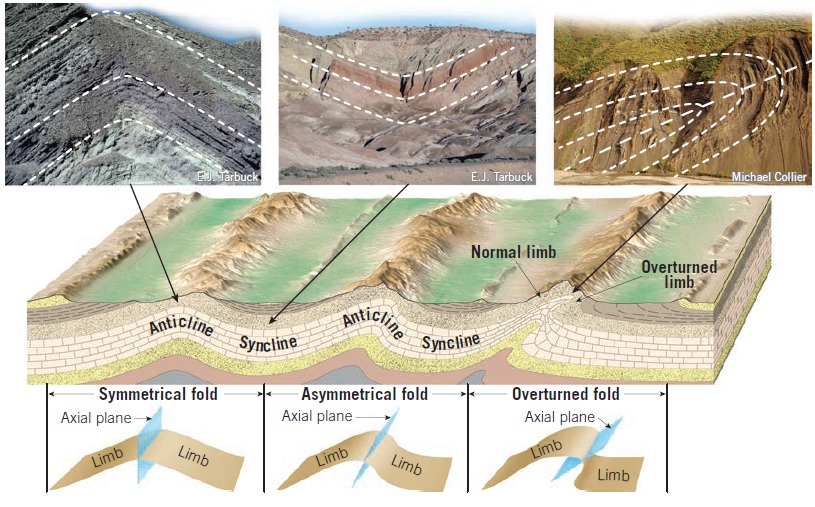
Anticlines occur when compressional stresses squeeze sedimentary layers into arch-like folds. These upfolded structures are sometimes spectacularly displayed along highway roadcuts that pass through deformed strata.
Typically found in association with anticlines are trough-like structures called synclines. Notice in Figure 1 that the right limb of the syncline is also the left limb of the adjacent anticline.
Depending on their orientation, these basic folds are described as symmetrical when the limbs are mirror images of each other and asymmetrical when they are not. An asymmetrical fold is said to be overturned if one or both limbs are tilted beyond the vertical. An overturned fold can also “lie on its side” so the axial plane is horizontal. These recumbent folds are common in highly deformed mountainous regions such as the Alps.
Folds also can be tilted by tectonic forces that cause their hinge lines to slope rather than have a horizontal orientation (Figure 2A). Folds of this type are called plunging folds because the hinge lines of the fold dip downward (plunge) and penetrate Earth’s surface.
Figure 2B shows the outcrop pattern produced when erosion removes the upper layers of a plunging anticline and exposes its interiors. Note that the outcrop pattern of an eroded anticline “points” in the direction it is plunging. The opposite is true for a syncline, which exhibits an outcrop pattern that points in the opposite direction of its plunge.
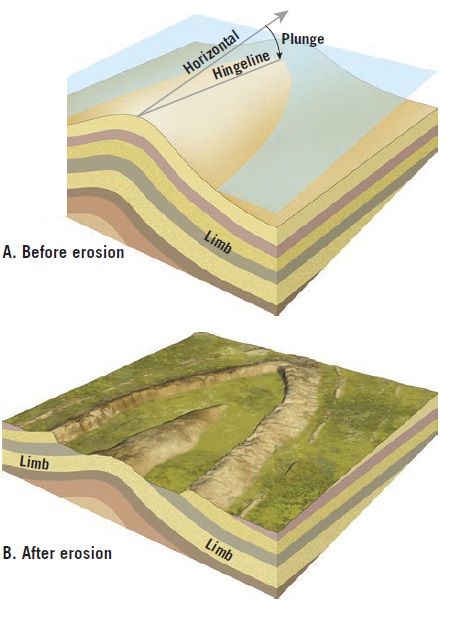
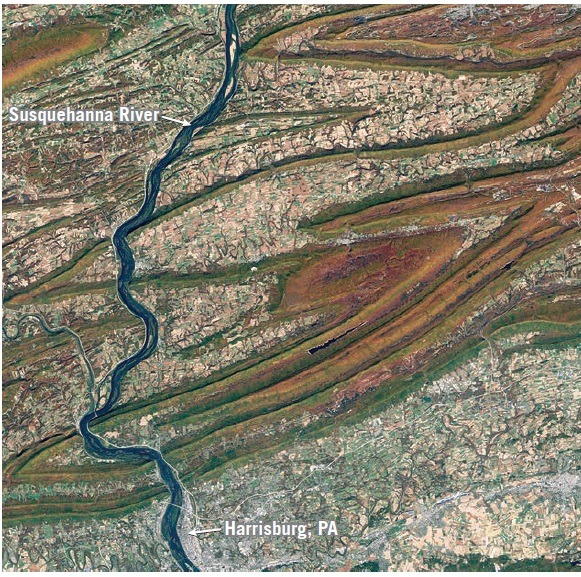
A good example of topography that results when erosional forces attack folded sedimentary strata is found in the Valley and Ridge Province of the Appalachians (Figure 3). It is important to recognize that ridges are not necessarily associated with anticlines, nor are valleys related to synclines. Rather, ridges and valleys result because of differential weathering and erosion. In the Valley and Ridge Province, for instance, resistant sandstone beds remain as imposing ridges separated by valleys cut into more easily eroded shale or limestone beds.

What causes anticlines and synclines?
Anticlines and synclines are structural features in geology that form as a result of tectonic forces acting on the Earth’s crust. These features are commonly associated with the folding of rock layers. Here are the main reasons for the formation of anticlines and synclines:
-
Tectonic Plate Movement:
- Anticlines and synclines are often formed as a result of compressional forces generated by the movement of tectonic plates. When two tectonic plates converge, one may be forced over the other, causing the rocks in the Earth’s crust to fold and buckle.
-
Compression and Folding:
- Compression is a key factor in the formation of both anticlines and synclines. The intense pressure resulting from the collision of tectonic plates causes the rocks to deform, leading to the upward folding of layers (anticlines) and the downward folding of layers (synclines).
-
Strain and Deformation:
- The strain caused by tectonic forces leads to the deformation of the Earth’s crust. Rocks respond to this strain by bending and folding, resulting in the formation of anticlines and synclines.
-
Brittle and Ductile Behavior:
- Rocks can exhibit both brittle and ductile behavior under stress. Brittle deformation leads to the fracturing and faulting of rocks, while ductile deformation results in folding. Anticlines and synclines are examples of ductile deformation where rocks bend rather than break.
-
Nature of Sedimentary Rocks:
- Anticlines and synclines are often associated with sedimentary rock layers. Sedimentary rocks, such as limestone and shale, are more prone to folding due to their generally more ductile nature compared to igneous or metamorphic rocks.
-
Isostatic Adjustments:
- The Earth’s crust is in a constant state of isostatic adjustment, seeking balance under various loads. Tectonic forces can cause changes in the thickness and density of the crust, leading to the folding of rock layers into anticlines and synclines.
-
Regional and Local Factors:
- Local variations in the geology, such as the presence of weak or ductile layers, can influence the formation of anticlines and synclines. Regional factors, including the overall stress and strain distribution in an area, also play a role.
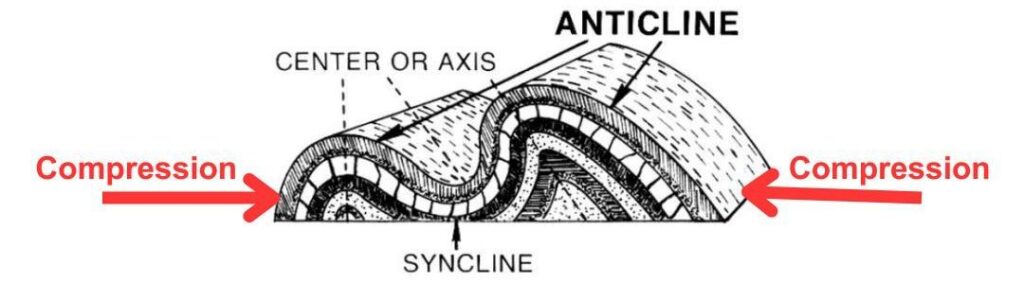
In summary, the primary cause of anticline and syncline formation is the tectonic forces resulting from the movement of Earth’s lithospheric plates. These forces lead to the deformation of rock layers, resulting in the characteristic folding observed in anticlines and synclines.





