Unraveling the Geological Joints

Introduction
In the dynamic field of geology, one of the most intriguing phenomena is the occurrence of geological joints, also known as rock fractures. Geological joints play a significant role in shaping the Earth’s crust and have a profound impact on various geological processes. In this article, we will delve into the world of geological joints, understanding their formation, types, and their importance in geology.
What are Geological Joints?
Geological joints are fractures in rocks along which no appreciable displacement has occurred. Unlike faults, which involve movement along the fracture, joints are fractures where the two sides of the rocks remain relatively fixed. They are widespread in the Earth’s crust and are prevalent in various rock types.
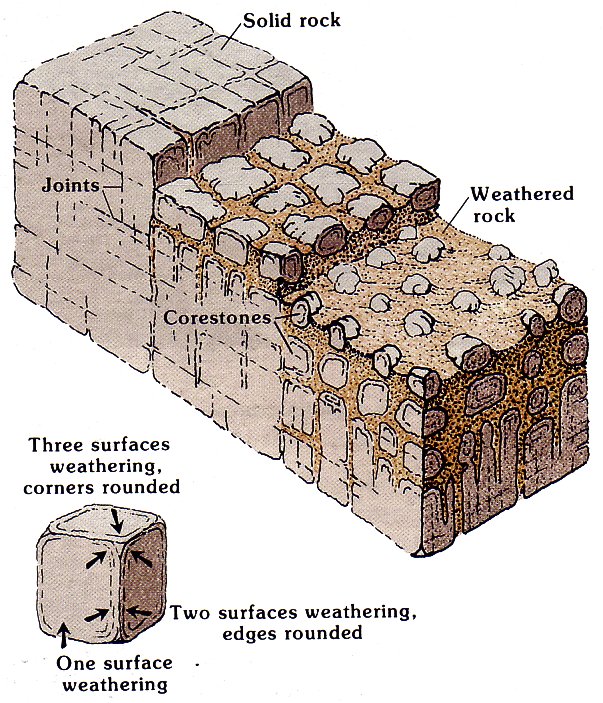
Types of Geological Joints
Columnar Joints
One of the most striking types of geological joints is the columnar joints, commonly observed in igneous rocks. They form during the cooling of lava or magma, which results in shrinkage fractures that produce elongated, pillar-like columns. Famous examples of columnar joints can be found at the Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland.

(Photo by Steve Hillebrand, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service)
Brittle Fracture
Brittle fractures are the most common type of geological joints and are caused by the failure of rocks due to stress. As rocks undergo deformation, they reach their breaking point and crack, forming fractures. These fractures are prevalent in the outermost crust and are crucial in accommodating tectonic stresses.
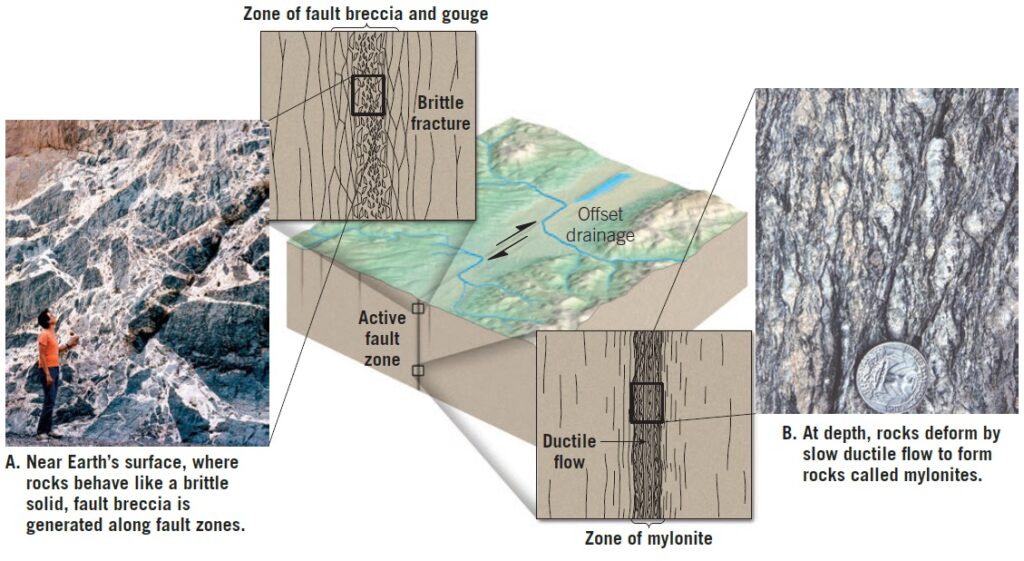
Tectonic Joints
Tectonic joints are formed in response to regional upwarping and downwarping of the Earth’s crust. As the crust undergoes subtle movements, it experiences stress, leading to the development of joint patterns. These joints provide valuable information about the tectonic history of a region.
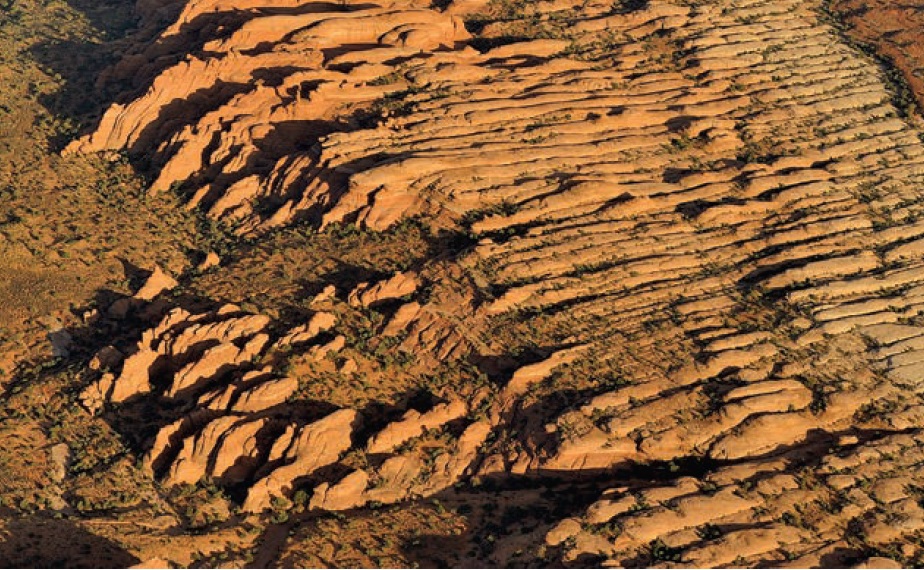

Influence of Geological Joints
Weathering and Erosion
Geological joints play a vital role in weathering and erosion processes. As water infiltrates the fractures, it accelerates the breakdown of rocks, leading to the formation of valleys, canyons, and other landforms.
Groundwater Movement
Joint patterns influence how groundwater moves through the Earth’s crust. Depending on the orientation and density of joints, groundwater can either flow freely or be impeded, affecting the formation of aquifers and the availability of water resources.
Economic Significance of Geological Joints
Mineral Deposits
Some of the world’s largest and most important mineral deposits are associated with geological joints. Hydrothermal solutions, mineral-rich fluids, migrate into fractured host rocks and precipitate valuable minerals such as copper, gold, silver, and uranium.
Challenges and Risks
Engineering Challenges
Highly jointed rocks can pose challenges to construction projects, including bridges, dams, and highways. The presence of joints increases the risk of rock instability and can lead to potential engineering failures.
Conclusion
Geological joints are a fascinating aspect of geology that offers valuable insights into the Earth’s crust. From columnar joints formed during cooling of igneous rocks to tectonic joints reflecting regional tectonic movements, these fractures have a significant impact on the geological processes that shape our planet. Understanding the influence of geological joints on weathering, groundwater movement, and mineral deposits is crucial for geologists and engineers alike in comprehending Earth’s dynamic history.
Keywords:
Geological joints, rock fractures, columnar joints, brittle fractures, tectonic joints, weathering, erosion, groundwater movement, mineral deposits, engineering challenges, geology.
