Landslide Investigation: A Comprehensive Guide for Geologists

Introduction:
Landslides are geological hazards that have been known to cause significant damage to infrastructure, loss of life, and economic losses. To mitigate these hazards, geologists carry out investigations to assess the risks of landslides, evaluate their causes, and develop effective management strategies. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of landslide investigations, including their significance, types, causes, investigation methods, and management strategies.
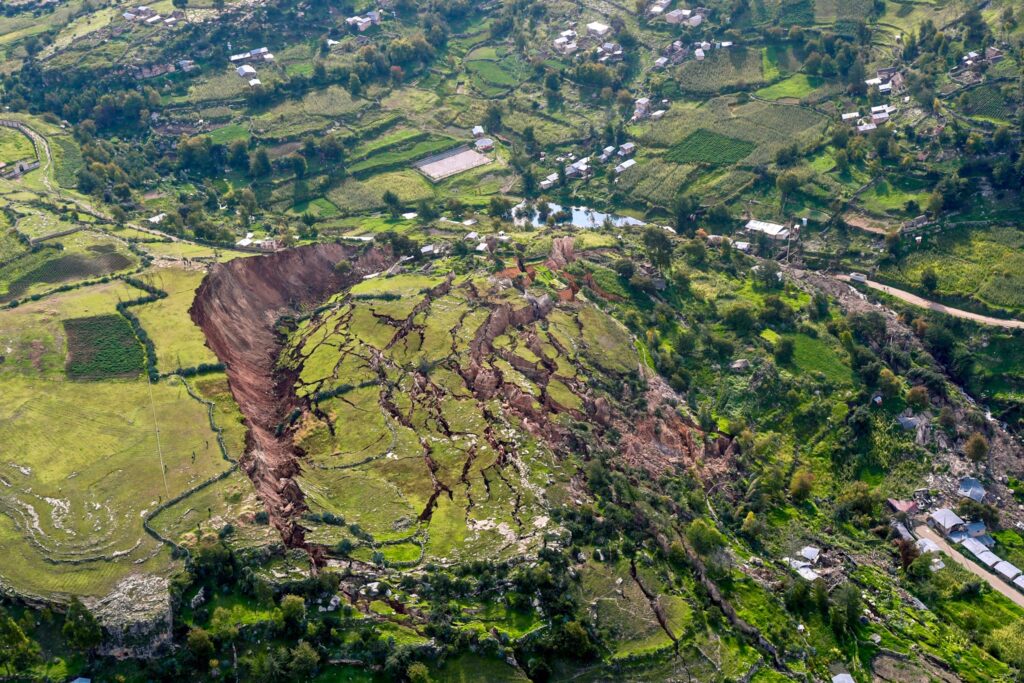

What are landslides, and why are they important?
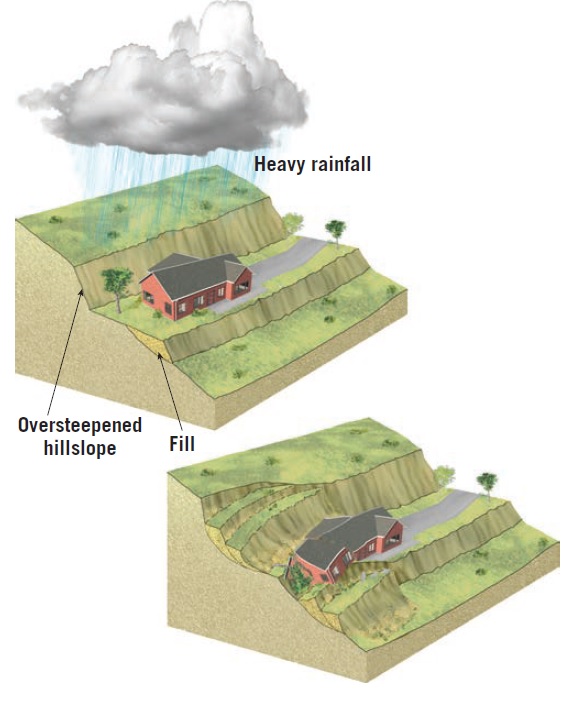
Landslides are the movement of rocks, soil, or debris down a slope or a hill. They occur when the stability of a slope is compromised, leading to the downslope movement of material. Landslides can be triggered by several factors, such as natural events (earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, heavy rainfall), human activities (excavation, construction, deforestation), and geological factors (slope angle, rock type, soil properties). The significance of landslide investigations lies in their ability to assess the potential risks of landslides, identify their causes, and develop effective management strategies to prevent their occurrence or minimize their impact.
Types of landslides:
Landslides can be classified into several types, depending on the nature of the movement, the material involved, and the mechanism of the movement. The most common types of landslides include rockfalls, debris flows, rotational slides, and translational slides. Rockfalls occur when rocks detach from a slope and fall freely down a hill. Debris flows involve the movement of a mixture of soil, rocks, and water down a slope. Rotational slides occur when the slope fails along a curved surface, causing the material to move downslope. Translational slides involve the failure of a slope along a planar surface, leading to the horizontal movement of material.
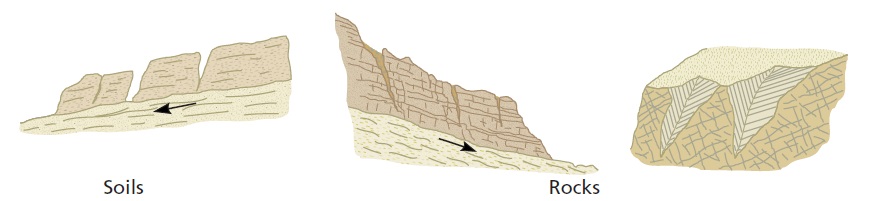
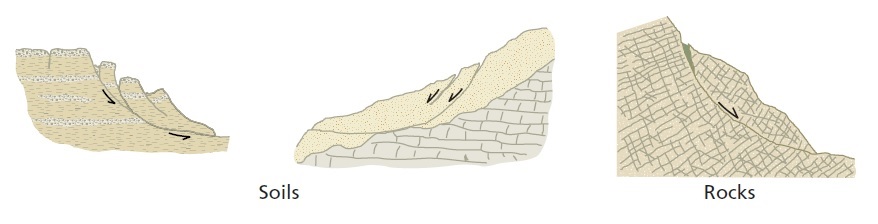
Causes of landslides:
Landslides can be triggered by various factors, such as geological, natural, and human activities. Geological factors include the slope angle, rock type, soil properties, and groundwater conditions. Natural factors include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, heavy rainfall, and erosion. Human activities, such as excavation, construction, and deforestation, can also destabilize slopes and trigger landslides. It is essential to identify the root cause of a landslide to develop effective management strategies to prevent their occurrence or minimize their impact.
Investigation methods:
Geologists use various methods to investigate landslides, such as field surveys, remote sensing, and laboratory testing. Field surveys involve visiting the landslide site, mapping the affected area, and collecting data on the slope angle, rock type, soil properties, and groundwater conditions. Remote sensing methods include satellite imagery, aerial photography, and LiDAR scanning to identify landslide features, such as cracks, scars, and displaced material. Laboratory testing involves analyzing soil and rock samples to determine their strength and stability.
Management strategies:
Effective management of landslides involves a combination of mitigation measures, such as avoidance, engineering, and land-use planning. Avoidance measures involve identifying areas prone to landslides and avoiding development in those areas. Engineering measures include the stabilization of slopes, construction of retaining walls, and installation of drainage systems. Land-use planning involves zoning and regulation of development in landslide-prone areas. Education and awareness campaigns can also help to reduce the risks of landslides by informing the public about the dangers of living or working in landslide-prone areas.
Conclusion:
Landslide investigations are essential for assessing the risks of landslides, identifying their causes, and developing effective management strategies to prevent their occurrence or minimize their impact. Geologists use various methods, such as field surveys, remote sensing, and laboratory testing, to investigate landslides. Effective management of landslides involves a combination of mitigation measures, such as avoidance, engineering, and land-use planning. With the increasing population and development in landslide-prone areas, it is crucial to prioritize the investigation and management of landslides to prevent or minimize their impact.
As geologists continue to investigate landslides, new technologies and methods are being developed to improve our understanding of these geological hazards. For example, the use of drones and other unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has proven to be effective in mapping and monitoring landslides, providing accurate and detailed data for analysis. Additionally, advances in modeling software have allowed geologists to simulate landslides, predict their behavior, and test the effectiveness of mitigation measures.
In conclusion, the investigation of landslides is a crucial aspect of geology, and it requires a multidisciplinary approach to be effective. By understanding the causes, types, and mechanisms of landslides, geologists can develop effective management strategies to mitigate the risks and reduce the impact of these geological hazards. With the continued advancement of technology and the increasing threat of climate change, the investigation and management of landslides will continue to be a critical area of study for geologists and other scientists.
