Rockslide: Causes, Effects, and Prevention

Introduction
In the world of geology, the term “rockslide” is one that commands attention. It’s a natural phenomenon that can have devastating consequences, not only for the environment but also for human communities in its path.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the topic of rockslides, exploring their causes, effects, and the crucial measures to prevent them. By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of what rockslides are and how they impact our planet.
What is a Rockslide?
A rockslide is a type of mass wasting event in which large volumes of rocks, debris, and soil suddenly move downhill, often with tremendous force and speed. These events can vary in scale from minor rockfalls to catastrophic avalanches of rock and debris that can bury entire landscapes.
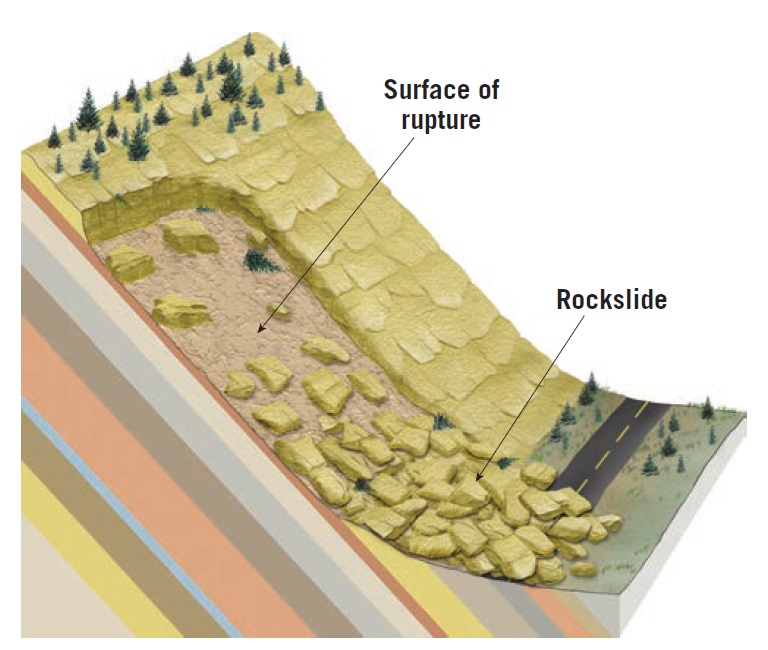
Rockslides are primarily triggered by a combination of geological factors, environmental conditions, and sometimes human activities. Understanding the causes of rockslides is crucial in mitigating their destructive impact.
Causes of Rockslides
Weathering and Erosion
One of the primary natural causes of rockslides is weathering and erosion. Over time, rocks become weakened by various weathering processes, such as freeze-thaw cycles, chemical weathering, and abrasion. As rocks deteriorate, they are more likely to break loose and descend downhill during heavy rainfall or seismic activity.
Geological Faults
Geological faults, especially active ones, can significantly contribute to the occurrence of rockslides. The movement along fault lines can dislodge rocks and create conditions where a sudden release of energy leads to a rockslide.
Human Activities
Human activities, such as construction, mining, and deforestation, can disturb the natural stability of slopes. Poor land management and inadequate infrastructure planning can increase the risk of rockslides in areas prone to these activities.
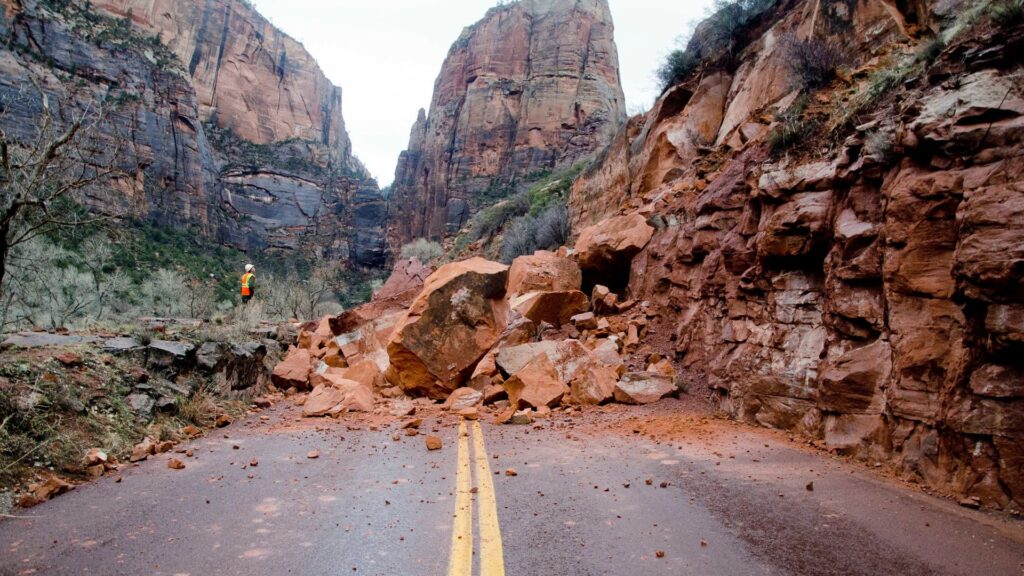

Effects of Rockslides
Rockslides can have devastating effects on both the environment and human settlements. Some of the key consequences include:
- Loss of Life: Rockslides can result in fatalities when they occur in populated areas or on roadways.
- Property Damage: Homes, infrastructure, and farmland can be destroyed or buried under massive rockslides.
- Environmental Impact: The disruption of natural ecosystems and watercourses can lead to long-term ecological damage.
- Economic Costs: Recovery and reconstruction efforts can place a significant financial burden on communities.
Preventing Rockslides
Preventing rockslides requires a multi-faceted approach, involving geological assessment, engineering solutions, and ongoing monitoring.
Structural Engineering
- Rockfall Barriers: Installing rockfall barriers along vulnerable slopes can intercept falling rocks and prevent them from reaching lower areas.
- Retaining Walls: Constructing retaining walls can stabilize slopes and reduce the risk of rockslides.
- Rock Bolting: Reinforcing rocks with rock bolts can help secure them in place.
Monitoring Systems
- Geotechnical Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of slope stability using instruments like inclinometers and piezometers can provide early warning signs.
- Seismic Sensors: Detecting seismic activity can be crucial in predicting potential rockslides.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite and drone technology can aid in assessing slope conditions and changes.
Vegetation Management
- Afforestation: Planting trees and vegetation on slopes can enhance soil stability and reduce erosion.
- Regular Maintenance: Clearing vegetation that may destabilize slopes or obstruct monitoring efforts is essential.
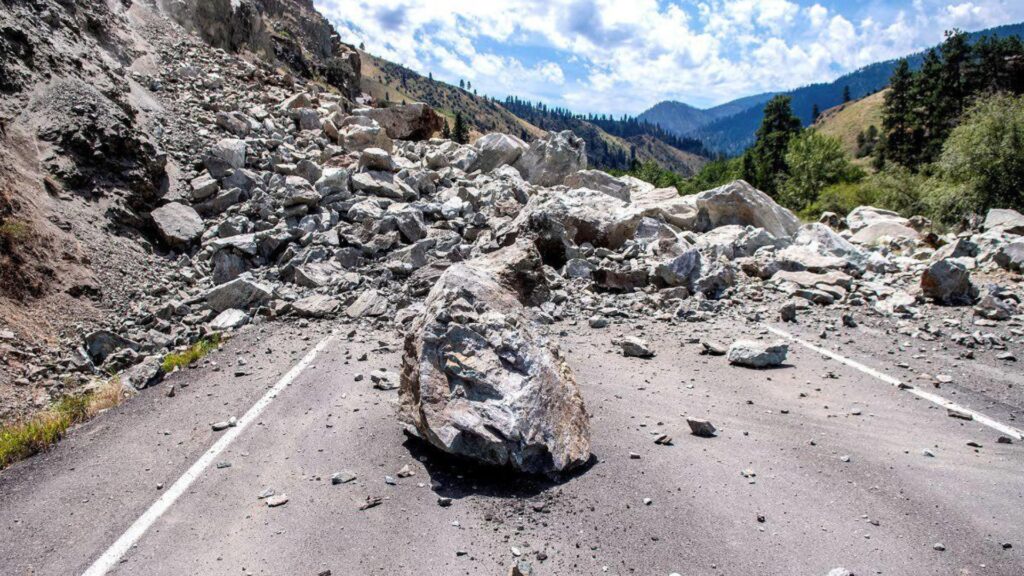

Famous Rockslides
- The Gros Ventre Slide: This massive rockslide occurred in Wyoming in 1925, damming the Gros Ventre River and forming Lower Slide Lake.
- The Hope Slide: In 1965, a devastating rockslide in British Columbia, Canada, buried a portion of the Hope-Princeton Highway.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what rockslides are and their underlying causes is vital for safeguarding our communities and natural landscapes. By implementing effective prevention measures and harnessing the power of structural engineering and monitoring systems, we can reduce the risks associated with rockslides and mitigate their devastating effects.
Rockslides remind us of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our planet’s geology, urging us to be proactive in preserving the safety of our environment and those who inhabit it.
