Shallow foundations

Shallow foundations represent a crucial element in structural engineering, serving as the interface between the structure and the underlying soil. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of shallow foundations, covering their definition, types, applications, and design principles, while drawing upon verified sources and expert insights.
Understanding Shallow Foundations
Definition and Function
Define shallow foundations as structural elements that transmit building loads to the earth’s surface, usually located at shallow depths beneath the ground level. Discuss their primary function of distributing loads efficiently while ensuring stability.
Mechanics of Load Transfer
Explore the mechanisms by which shallow foundations transfer loads, including bearing capacity, settlement, and soil-structure interaction. Emphasize the importance of understanding soil behavior and foundation response.
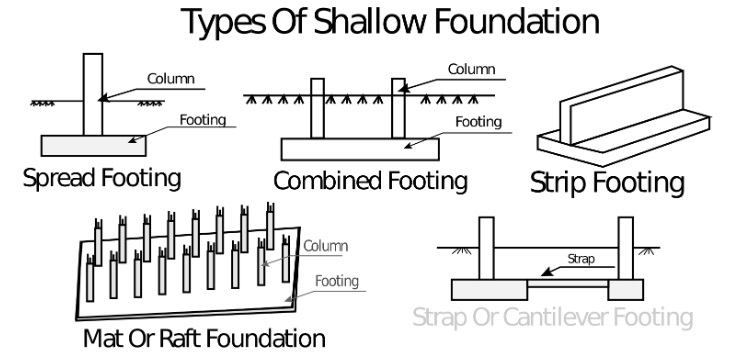
Types of Shallow Foundations
Shallow foundations play a critical role in transferring building loads to the ground efficiently. Understanding the different types of shallow foundations is essential for designing structures that are stable and durable. Here are the four primary types:
1. Spread or Isolated Footing
Definition: Spread footings, also known as isolated footings, are one of the most common types of shallow foundations. They distribute the load of a single column or pedestal to the soil beneath.
Design Considerations:
- Shape: Spread footings come in various shapes, including rectangular, square, circular, or trapezoidal, depending on the shape and size of the column they support.
- Depth: The depth of spread footings is typically shallow, extending just below the frost line or the active zone of soil.
Applications: Spread footings are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial construction for supporting individual columns, pillars, or posts.
2. Strip Foundation
Definition: Strip foundations, also known as continuous footings, are elongated concrete strips that support multiple columns along their length. They distribute the load of several adjacent columns over a wider area.
Design Considerations:
- Width: Strip foundations are wider than spread footings and may vary in width based on the number and spacing of columns they support.
- Thickness: The thickness of strip foundations is determined based on the applied loads and soil bearing capacity.
Applications: Strip foundations are commonly employed in buildings with closely spaced columns, such as load-bearing masonry walls or row houses.
3. Mat or Raft Foundation
Definition: Mat foundations, also known as raft foundations, are large reinforced concrete slabs that cover the entire footprint of a building. They distribute the building loads over a wide area to reduce the pressure on the underlying soil.
Design Considerations:
- Thickness: Mat foundations are thicker compared to other shallow foundations to spread the loads effectively.
- Reinforcement: Due to their large size, mat foundations require significant reinforcement to withstand bending and shear forces.
Applications: Mat foundations are suitable for structures with heavy loads, variable soil conditions, or a high water table, such as high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, or structures built on soft or expansive soils.
4. Combined Foundation
Definition: Combined foundations integrate elements of different types of shallow foundations to optimize load distribution and accommodate specific site conditions.
Design Considerations:
- Integration: Combined foundations may combine elements of spread, strip, and mat foundations based on the structural requirements and soil characteristics.
- Customization: The design of combined foundations is tailored to address the unique challenges of a particular construction project.
Applications: Combined foundations are utilized in complex building designs or challenging soil conditions where a single type of shallow foundation may not suffice to support the structure adequately.
Applications and Suitability
Residential Construction
Examine the use of shallow foundations in residential buildings, emphasizing their suitability for low to medium-rise structures and the importance of site-specific analysis.
Commercial and Industrial Projects
Discuss the application of shallow foundations in commercial complexes, warehouses, and industrial facilities, considering factors such as heavy equipment loads and environmental conditions.
Design Principles and Considerations
Geotechnical Investigation
Highlight the significance of thorough geotechnical investigation, including soil testing and analysis, to assess soil properties and foundation requirements accurately.
Bearing Capacity Analysis
Explain the process of determining bearing capacity using empirical methods and advanced geotechnical engineering principles, ensuring the adequacy of foundation support.
Structural Design and Reinforcement
Discuss the structural design of shallow foundations, considering factors such as load combinations, safety factors, and reinforcement detailing to enhance durability and performance.

Advantages, Limitations, and Sustainability
Advantages
Enumerate the advantages of shallow foundations, including cost-effectiveness, ease of construction, and minimal disturbance to the site.
Limitations and Challenges
Address the limitations of shallow foundations, such as limited load-bearing capacity and susceptibility to differential settlement, along with strategies to mitigate risks.
Sustainability Considerations
Discuss the role of shallow foundations in sustainable construction practices, including techniques for minimizing environmental impact and enhancing long-term resilience.
Conclusion
Summarize the key insights presented in the guide, emphasizing the importance of integrating geotechnical engineering principles and structural design considerations to achieve safe and efficient shallow foundation systems in diverse construction projects.
