Tourmaline Pegmatite

Introduction
When it comes to fascinating geological formations, tourmaline pegmatite stands out as a captivating subject. This remarkable rock exhibits a felsic composition akin to granite, boasting more than 20 percent quartz and over 65 percent total silica content. While its primary constituents include gray quartz, pink K-feldspars, and dark biotite mica, the star of the show is undoubtedly the exquisite borosilicate mineral, tourmaline.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of tourmaline pegmatite, exploring its characteristics, formation, and significance in the realm of geology.
Understanding Tourmaline Pegmatite
Tourmaline pegmatite is a rock that stands out due to its distinct composition and captivating features. Here, we will take a closer look at its key attributes:
| Group | IGNEOUS |
| Origin | Intrusive |
| Grain size | Very coarse |
| Crystal shape | Euhedral |
| Classification | Felsic |
| Occurrence | Pluton, Dyke, Sill |
| Color | Light |
Composition
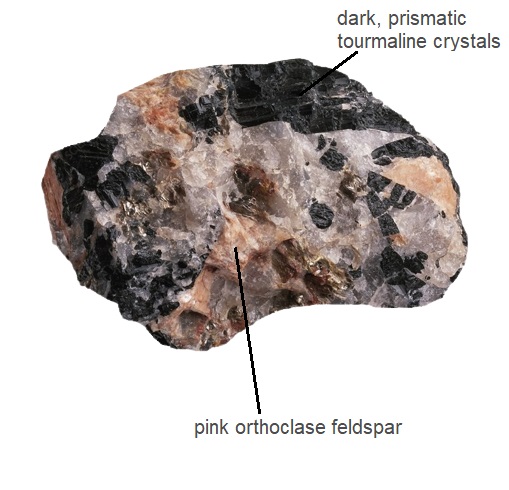
Tourmaline pegmatite shares a felsic composition, akin to granite. Its mineral content comprises more than 20 percent quartz and a staggering 65 percent total silica. Within its matrix, one can commonly find gray quartz, pink K-feldspars, and dark biotite mica. However, it is the presence of tourmaline, a borosilicate mineral, that truly defines this rock.
Texture
The texture of tourmaline pegmatite is characterized by its coarse-grained crystals, making it a captivating specimen for geologists and mineral enthusiasts alike. Some of the larger crystals within this rock can reach impressive lengths of 2 to 2.5 inches (5 to 6 cm). Moreover, these crystals often exhibit well-defined euhedral shapes. In particular, the tourmaline crystals found within this rock form coarse, striated prismatic structures, adding to its allure.
Formation of Tourmaline Pegmatite
The formation of tourmaline pegmatite is a complex geological process that involves several key factors. To better understand how this remarkable rock comes into existence, let’s explore the factors that contribute to its formation:
1. Parent Magma
Tourmaline pegmatite begins its journey as a part of a parent magma body. This magma, which is felsic in composition, contains the necessary elements and minerals that will later crystallize to form tourmaline pegmatite.
2. Cooling Rate
The cooling rate of the parent magma is crucial in the formation of tourmaline pegmatite. The slower the cooling rate, the larger the crystals that can form. This gradual cooling allows for the growth of sizable quartz, K-feldspar, and tourmaline crystals within the pegmatite.
3. Mineral Precipitation
As the magma cools, minerals start to precipitate out of the molten rock. The borosilicate mineral tourmaline crystallizes within the pegmatite, forming its characteristic prismatic crystals.
4. Hydrothermal Activity
Hydrothermal fluids also play a significant role in the formation of tourmaline pegmatite. These fluids can introduce additional elements and minerals into the pegmatite, contributing to its overall composition.
Significance in Geology
Tourmaline pegmatite is of great significance in the field of geology for several reasons:
1. Indicator of Rare Elements
Due to its unique formation process, tourmaline pegmatite can contain concentrations of rare and valuable elements such as lithium, beryllium, and tantalum. Mining operations often target these pegmatites in search of these economically valuable resources.
2. Gemstone Potential
Tourmaline crystals found within pegmatites can be of gem-quality. They are sought after by jewelers and collectors for their vibrant colors and unique properties. Some tourmaline pegmatites are famous for producing exquisite gemstones.
3. Geological Research
Studying tourmaline pegmatite provides valuable insights into the geological processes involved in the formation of such intricate and mineral-rich rocks. Researchers use these formations to better understand the Earth’s geological history.
Conclusion
Tourmaline pegmatite is a captivating geological formation with a rich composition and fascinating texture. Its unique characteristics, including the presence of borosilicate tourmaline crystals, make it a subject of great interest for geologists, mineral enthusiasts, and the mining industry.
In this article, we’ve explored the composition, texture, formation process, and significance of tourmaline pegmatite in the world of geology. Its role as an indicator of rare elements, potential for gemstone production, and contribution to geological research highlight the importance of this intriguing rock formation in the field of earth sciences.
Next time you come across a tourmaline pegmatite or hear about its geological significance, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for the complex processes that have shaped this remarkable rock.
Read more on blog: