Types of aquifer by texture

Aquifers can be classified based on their texture, which refers to the size and arrangement of the grains or particles that make up the aquifer material. The texture of an aquifer greatly influences its porosity and permeability, which in turn affect the movement and storage of water within the aquifer. Here are the main types of aquifers classified by texture:
Coarse Detrital Aquifer:
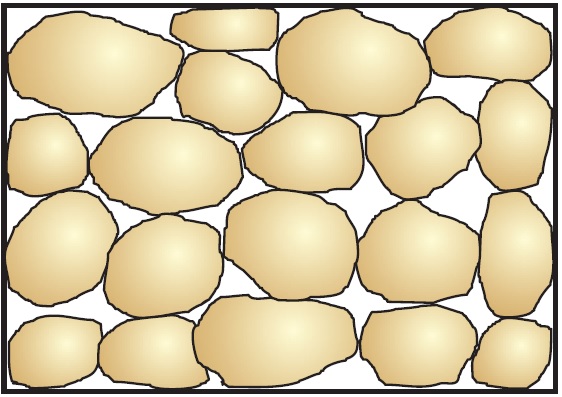
This aquifer consists of predominantly coarse-grained materials such as sand and gravel. These materials typically have high permeability due to the larger pore spaces between the grains.
Coarse Detrital Aquifer with Silt Matrix:
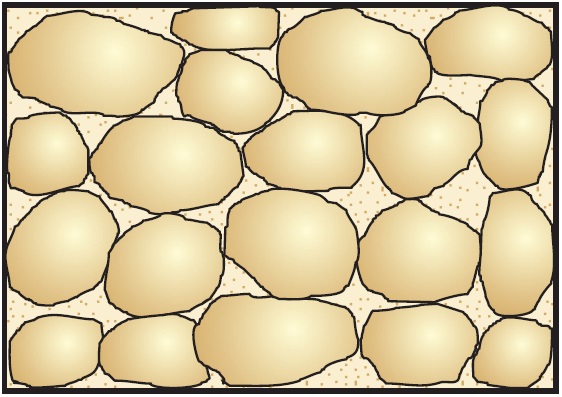
This aquifer is similar to the coarse detrital aquifer but contains a matrix of silt-sized particles. The presence of silt can affect permeability compared to a purely coarse-grained aquifer.
Coarse Detrital Aquifer with Clay Matrix:
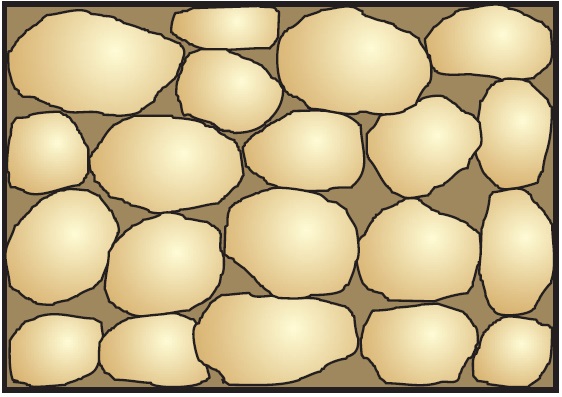
Similar to the previous types, this aquifer has a coarse-grained framework, but the matrix is composed of clay-sized particles. The presence of clay can significantly reduce permeability.
Coarse Detrital Aquifer with Porous Grains:
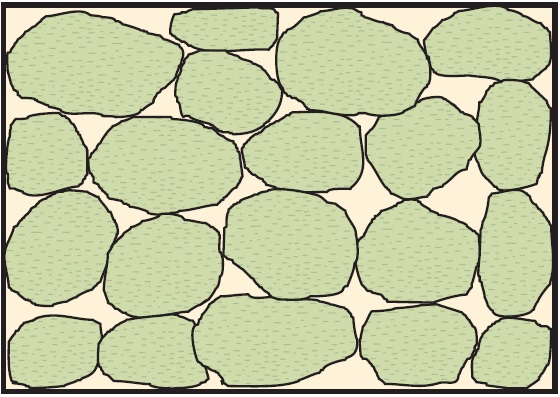
In this type of aquifer, the coarse-grained materials have inherent porosity within the grains themselves, further contributing to water storage and movement.
Fissured Aquifer:
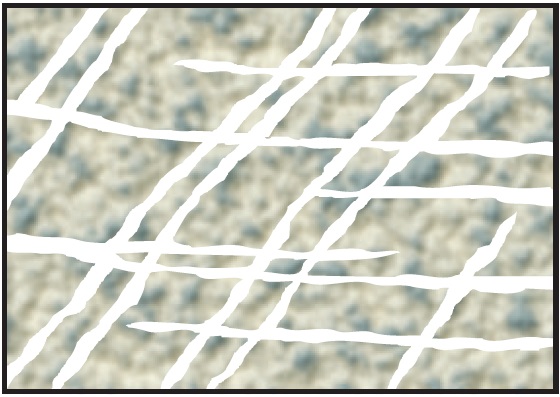
Fissured aquifers are characterized by fractures and fissures in the rock, which can serve as high-permeability pathways for water flow. These fractures greatly influence the aquifer’s overall permeability.
Karstic Aquifer:
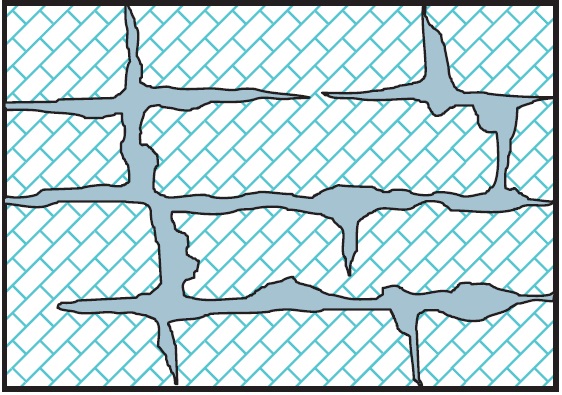
Karstic aquifers are formed in limestone or other soluble rock formations. They are characterized by unique features such as sinkholes, caves, and underground rivers, which provide rapid conduits for water movement.
Karstic and Porous Aquifer:
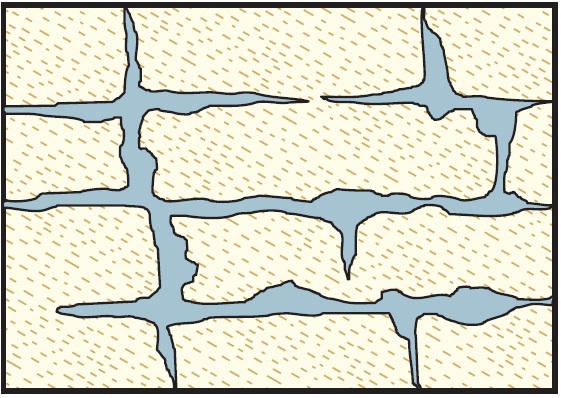
This type combines the characteristics of a karstic aquifer with inherent porosity in the rock material. It can lead to complex and rapid water flow patterns through both karst features and the porous rock matrix.
Each of these aquifer types has distinct properties that influence how water moves and is stored within the geological formations. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for managing water resources and groundwater systems effectively.
