Types of soils

Soil is a complex material, very variable both in chemical composition and particle size. Studying soils requires language and terminology that can be easily understood by specialists in different countries and in different fields. The particles which make up soils are therefore classified into four main groups, depending on their size:
Gravels: grain size between 8–10 cm and 2 mm with grains visible to the naked eye. Low water retention because of surface inactivity and large inter-particle spaces.
Sands: particle size between 2 and 0.060 mm, still recognizable with the naked eye. They do not form continuous aggregates when mixed with water and readily separate from it.
Silts: particle size from 0.060 to 0.002 mm. Some classifications give a lower value of 0.005 mm, but for practical purposes there is hardly any difference between the two. Better water retention than larger sized particles. A silt and water paste placed on the palm of the hand readily exudes water when tapped
Clays: formed from smaller particles than silt (0.002 mm) with gel-sized particles resulting from chemical changes. They are formed mainly from silicate minerals composed of chains of tetrahedral and octahedral elements (with the silicate ion at the centre of regular structures) and are joined by weak covalent bonds that allow water molecules to enter the chains. This may sometimes cause volume increases which return to their former state as the water evaporates. The resulting structure has a high water retention capacity with small interparticle spaces and a large absorbent particle surface area. As a result clays are generally problematic materials, requiring a long time for consolidation or expulsion of water under loads.
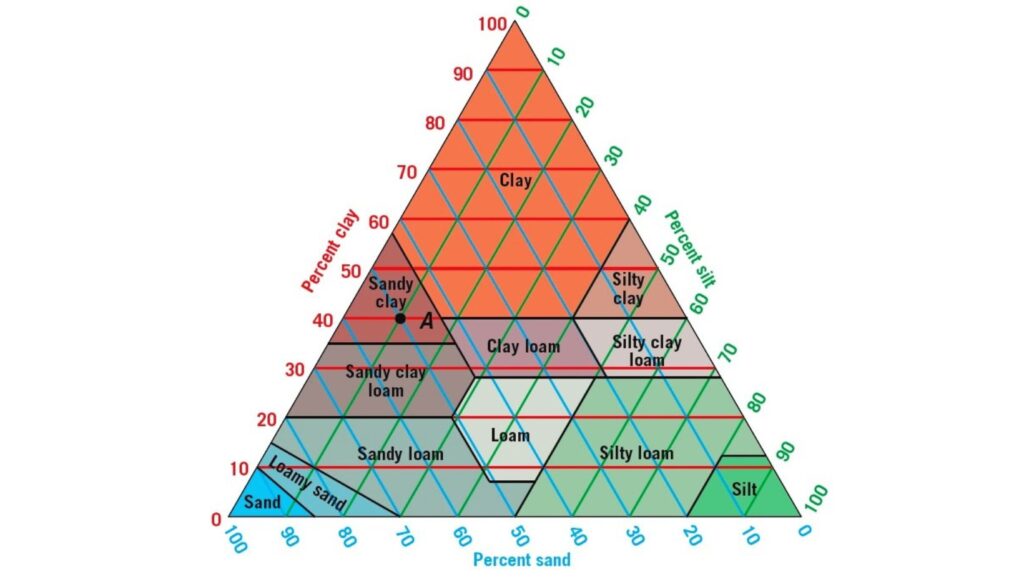
These particle sizes can be found naturally occurringm in various proportions, the percentages of which are defined by laboratory analyses and dictate a description of the soil.
