
Limestone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of calcium carbonate, is a fascinating geological formation that undergoes weathering over time. This article delves into the intricacies of the weathering processes affecting limestone, exploring both chemical and physical aspects. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of how weathering shapes limestone, we can appreciate its geological significance.
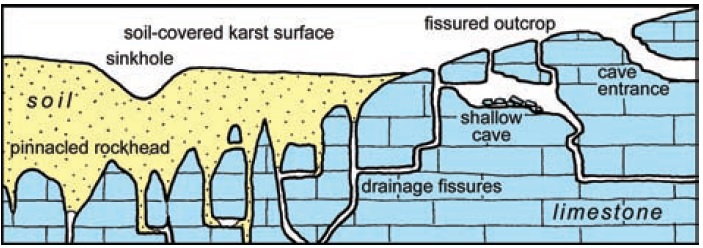
Chemical weathering plays a crucial role in altering the composition of limestone. The following factors contribute to the chemical weathering of limestone:
Carbonation is a prominent process where limestone reacts with carbon dioxide dissolved in water, forming calcium bicarbonate. This reaction weakens the structure of the rock, making it more susceptible to further weathering.
The impact of acid rain on limestone is significant. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere combine with rainwater, creating an acidic solution that erodes the surface of limestone. This process is particularly pronounced in areas with high industrial activity.
Limestone contains minerals susceptible to oxidation, such as pyrite. When these minerals react with oxygen, they undergo chemical changes, leading to the breakdown of the rock’s structure.
Physical weathering mechanisms contribute to the breakdown of limestone through various processes:
In regions with fluctuating temperatures, water seeps into cracks in limestone. As the water freezes and expands, it exerts pressure on the rock, causing it to fragment. Subsequent thawing widens the cracks, accelerating the weathering process.
Abrasion occurs when wind-blown sand and other particles erode the surface of limestone. This mechanical process smoothens the rock’s features and contributes to its overall degradation.
Biological factors, such as the growth of plant roots and burrowing organisms, can physically disrupt the integrity of limestone. Over time, the cumulative effect of biological weathering weakens the rock structure.
Understanding the weathering processes affecting limestone is essential for various reasons:
Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Many historical structures and monuments are constructed using limestone. Knowledge of weathering processes helps in the conservation and restoration of these cultural assets.
Environmental Impact: Awareness of limestone weathering contributes to our understanding of environmental changes, especially concerning issues like acid rain and climate fluctuations.
Geotechnical Considerations: Engineers and geologists use insights into limestone weathering to make informed decisions in construction projects, ensuring stability and durability.
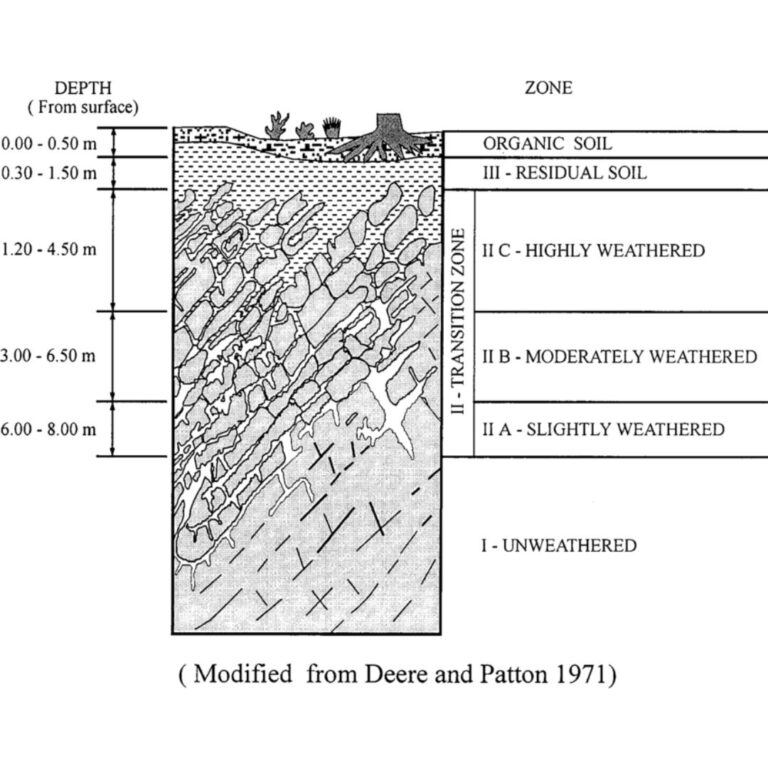
In conclusion, the weathering of limestone is a dynamic geological process influenced by both chemical and physical factors. This article has provided an in-depth exploration of these mechanisms, emphasizing their significance in various fields. As we continue to unravel the complexities of limestone weathering, we enhance our ability to preserve natural wonders and make informed decisions in engineering and environmental contexts.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |